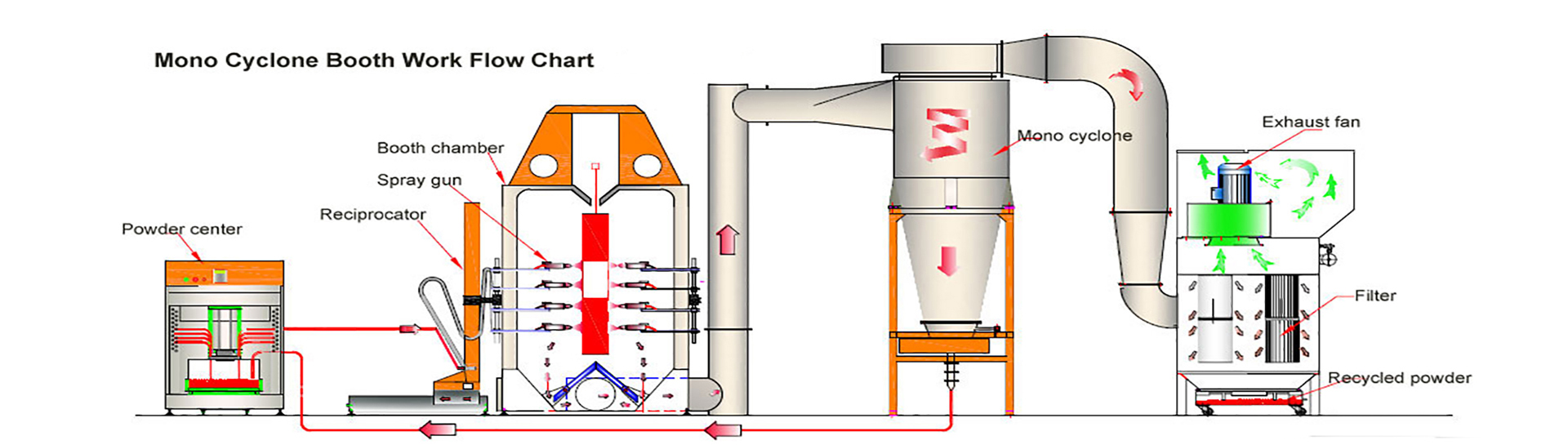
I. Core Definitions and Operating Principles
1. Powder Spray Booth
Definition: A powder spray booth is equipment specifically designed for electrostatic powder coating. It uses a high-voltage electrostatic field to evenly adsorb powder coating onto the workpiece surface, where it is cured at high temperatures to form a coating.
Operating Principle:
Electrostatic Adsorption: Powder coating is sprayed from a spray gun and evenly adheres to the grounded workpiece surface under the action of high-voltage static electricity.
Bake-Curing: After adsorption, the workpiece enters a heating furnace (180-220°C), where the powder melts and levelizes, forming a dense coating.
Powder Recovery: Unadsorbed powder is recovered through a filtration system (such as filter elements or bags) for recycling and minimizing waste.
2. Paint Spray Booth
Definition: A paint spray booth is equipment specifically designed for liquid paint spraying. It controls airflow and paint mist to ensure coating quality and environmental compliance.

Operating Principle:
Atomized Spray: Liquid paint is atomized by a spray gun, evenly covering the workpiece surface.
Drying and Curing: The coating cures through solvent evaporation (physical drying) or an oxidation reaction (such as baking). Paint Mist Treatment: Paint mist is captured using devices such as water curtains, dry filtration, or Venturi tubes to prevent contamination.
II. Structural Component Comparison
1. Powder Spray Booth Structure
Board Shell:
Constructed of steel or stainless steel, it offers excellent sealing and corrosion resistance, ensuring powder does not leak.
Filtration System:
Core components include filter elements or bags, which efficiently recover unabsorbed powder and reduce material costs.
Ventilation System:
A fan and air duct maintain negative pressure within the room, ensuring even distribution of powder and exhausting exhaust gases.
Lighting and Control System:
Explosion-proof lighting provides a clear view and automatically controls spray parameters (such as voltage and flow rate).
2. Spray Booth Structure
Board Structure:
Fully or semi-enclosed design, equipped with air supply and exhaust systems and a paint mist capture device.
Paint Mist Treatment System:
Wet Type: Water curtain, hydrocyclone, or spray, separating paint mist through water washing.
Dry Type: Utilizes paint mist felt, lime, or electrostatic filtration, eliminating the need for water. Water Supply System (Wet Process Only):
A circulating water pool treats paint-containing wastewater, requiring regular paint residue removal.
Lighting and Control Systems:
Explosion-proof lighting and temperature and humidity control ensure a stable painting environment.
III. Application Scenarios and Industry Compatibility
1. Powder Spray Booth Applications
High wear and corrosion resistance requirements:
Home appliance housings (such as refrigerators and washing machines), automotive parts (such as wheels and bumpers), and metal furniture (such as office desks and shelves).
Environmentally Stringent Applications:
Powder coatings offer low VOC emissions and comply with environmental regulations, making them suitable for industries such as electronics and medical devices.
High-Volume Production:
High powder recovery rates make them suitable for assembly line operations, such as hardware and architectural profiles.
2. Paint Spray Booth Applications:
Complex Surfaces and Decorative Effects:
Automobile bodies, artwork, and plastic products (such as toys and electronic product housings) requiring high gloss or special textures.
Multi-Material Compatibility:
Suitable for a variety of materials, including wood, plastic, and metal, and particularly well-suited for small-batch, diversified production. Repair and Color Change:
For applications such as automotive repair and architectural repainting, color and coating thickness can be flexibly adjusted.
IV. Advantages and Disadvantages
1. Coating Performance
Coatings produced in powder spray booths are known for their strong wear and corrosion resistance, strong adhesion, and excellent color stability, making them particularly suitable for long-term protection of metal workpieces. While coatings produced in spray booths are less hard and more easily scratched, they can achieve rich colors and adjustable gloss, meeting decorative needs.
2. Environmental Protection
Powder spray booths achieve over 95% material utilization through powder recovery systems, with near-zero VOC emissions, meeting strict environmental standards. Spray booths, on the other hand, must deal with paint mist and solvent volatilization, requiring exhaust gas treatment equipment such as activated carbon adsorption and catalytic combustion, resulting in higher environmental costs.
3. Application Efficiency
Powder spray booths are highly automated and suitable for large-scale production lines. A single spray coat is sufficient, resulting in significant efficiency. While spray booths offer flexibility, they require multiple coats and drying cycles, resulting in a longer overall cycle time. This efficiency advantage is particularly limited in small-batch production.
4. Maintenance Costs
Powder spray booths require regular cleaning of the powder recovery system (e.g., filters and bags), but overall maintenance requirements are minimal. Paint spray booths, on the other hand, require frequent paint residue removal and filter media replacement for their paint mist treatment systems (e.g., water curtains and dry filtration), resulting in higher maintenance frequency and costs.
5. Color Changes
Powder spray booths require thorough equipment cleaning when changing colors, which is time-consuming and more suitable for large-scale production of a single color. Paint spray booths offer convenient color switching, requiring only adjustments to the paint formula, making them ideal for small-batch, multi-color orders.
V. Environmental and Safety Considerations
1. Environmental Performance
Powder spray booths:
Powder recovery rates exceed 95%, and VOC emissions are virtually zero, meeting green production standards.
Paint spray booths:
Exhaust gas treatment technologies such as activated carbon adsorption and catalytic combustion are required to ensure emissions meet standards.
2. Safety
Powder spray booths:
Powder is flammable and requires explosion-proof electrical systems and dust concentration monitoring devices. Spray booths:
Solvents are flammable and explosive, requiring strict ventilation and fire prevention measures, including the installation of combustible gas alarms.
VI. Conclusion
Powder spray booths and paint spray booths each have their own advantages in industrial coating:
Powder spray booths are suitable for high-volume production of metal parts requiring high wear and corrosion resistance, and offer excellent environmental performance.
Spray booths are suitable for a variety of materials and decorative effects, flexibly meeting small-batch, personalized needs.
Companies should select the most suitable coating equipment based on the workpiece material, coating performance requirements, production scale, and environmental regulations. In the future, with advances in powder coating technology (such as low-temperature curing powders) and improvements in spray booth exhaust gas treatment technology, both will achieve an even better balance between environmental protection and efficiency.