Introduction
The machinery and equipment sector is embracing powder coating lines as a sustainable, high-efficiency alternative to traditional liquid coatings. Driven by environmental regulations and market demand for durable finishes, this technology offers transformative benefits for manufacturers. This article delves into its applications, emphasizing automation, sustainability, and alignment with international standards.
1. Industry Drivers for Adoption
1.1 Regulatory Compliance
Global policies, such as China’s "paint-to-powder" initiative and the EU’s RoHS/REACH directives, prioritize low-VOC solutions. Powder coating’s zero-emission advantage makes it ideal for compliance.
1.2 Technological Advancements
Innovations like robotic spray systems and low-temperature curing expand applicability. For example, intelligent lines now integrate 3D laser scanning and AI-driven quality control, enabling precision on complex parts.
1.3 Market Demand
Sectors like construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and electric vehicles require corrosion-resistant finishes. Powder coating excels in uniform coverage on intricate geometries.
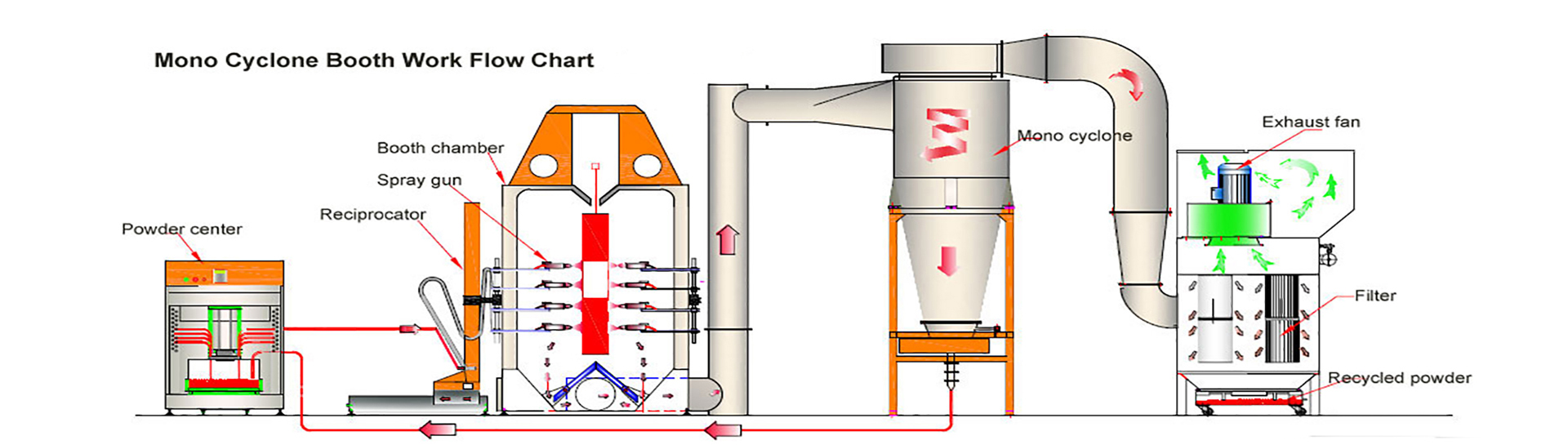
2. Core Technologies and Applications
2.1 Automated Spray Systems
Robotic Spray Guns: Electrostatic technology ensures even coating on irregular surfaces.
Conveyor Integration: Synchronized conveyors optimize workflow efficiency.
2.2 Low-Temperature Curing
Advanced resins enable curing at 120–160°C, reducing energy use by 30% for heat-sensitive parts.
2.3 High-Edge Coverage
Innovative pretreatment and powder formulations address sharp edges, ensuring full coverage and enhanced durability.
3. Process Optimization and Quality Control
3.1 Pretreatment Innovations
Ultrasonic Cleaning: Removes contaminants for superior adhesion.
Phosphate Conversion Coatings: Boost corrosion resistance for outdoor equipment.
3.2 Real-Time Monitoring
Inline gauges and AI vision systems detect defects per ASTM standards, reducing rework rates.
3.3 Certification Compliance
Automated systems streamline adherence to ISO 12944 (corrosion protection) and ISO 14001 (environmental management).
4. Global Market Strategies
4.1 Green Certifications
Products meeting CE marking and China Environmental Labeling facilitate market access in regulated regions.
4.2 Supply Chain Collaboration
Joint R&D between material suppliers and machinery producers ensures compatibility and performance optimization.
4.3 Case Study: Export Success
Partnerships in emerging markets demonstrate how localized technical support and compliance with regional standards drive export growth.
5. Future Directions
5.1 Digital Integration
AI predictive maintenance and IoT-enabled powder recovery systems minimize downtime.
5.2 Advanced Materials
TGIC-free polyesters and UV-curable powders expand applications in high-wear environments.
5.3 Circular Economy
Powder recycling initiatives align with sustainability goals, reducing raw material use by up to 95%.
Conclusion
Powder coating lines are redefining efficiency and sustainability in machinery manufacturing. By integrating automation, adhering to global standards, and prioritizing eco-friendly practices, manufacturers can achieve superior quality, regulatory compliance, and a competitive edge. As technology evolves, AI and advanced materials will further solidify powder coating’s role in the future of industrial production.
For machinery manufacturers targeting global markets, investing in powder coating automation is a strategic imperative to meet environmental and performance demands.